Romania: Second CEE central bank to raise key policy interest rates (Martin Ertl)
- The National Bank of Romania increased its key policy rate by 25 bp to 2 %.
- We expect inflation to have reached 3 % in Q4 2017 (3.2 % in November); 0.3 %-points above the latest NBR’s projection (November).
- Double digit growth of wages and unit labor costs in Q3 2017 have already indicated domestic price pressure to emerge.
- The 3-months interbank interest rate (ROBOR) has picked up significantly since September.
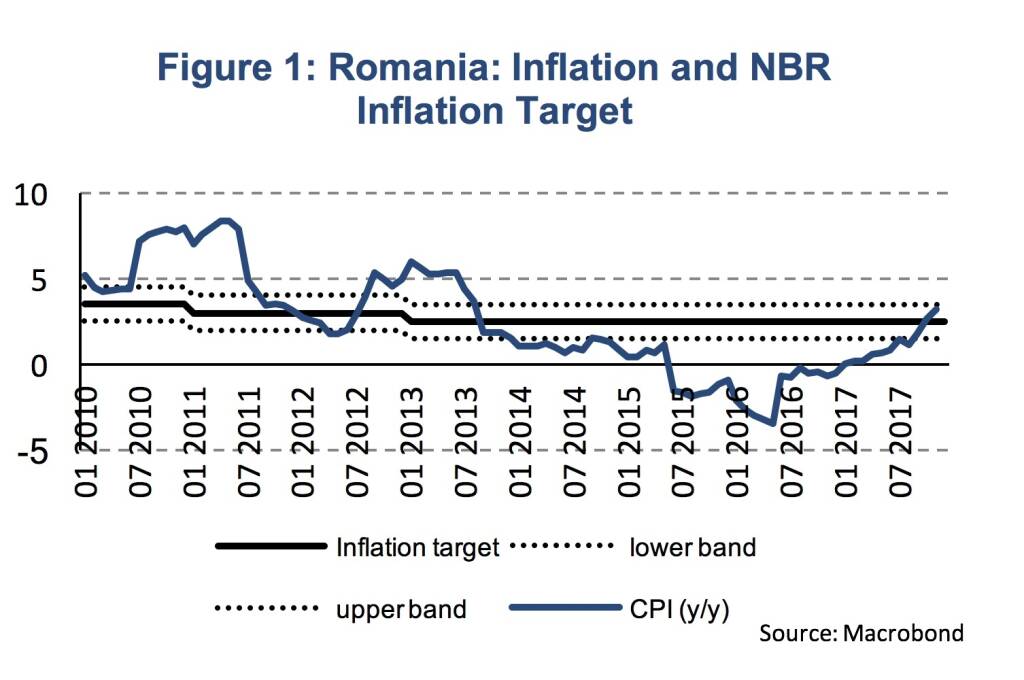
At its board meeting on the 8th of January, the National Bank of Romania (NBR) decided to raise its key policy rate by 25 basis points (bp) to 2 %. This is the second central bank in the CEE region, after the Czech Republic, to raise its key policy rate. The inflation-targeting central bank reacted to accelerating price pressure. In November, inflation was at 3.2 % (y/y), after 2.6 % in October and 1.8 % in September. The inflation target is set at 2.5 % with an upper band at 3.5 % (Figure 1).
With the next inflation projections being published in early February, the central bank acted based on the November inflation report. In November, the NBR expected inflation to be at 2.7 % in Q4 2017. The recent acceleration of consumer prices, however, suggest inflation to be 3 % in Q4 2017 and 1.3 % (y/y) for the whole year of 2017. Hence, domestic price pressures have emerged at a faster pace than the NBR expected, which motivated the central bank to increase its key policy rate for the first time since July 2008.
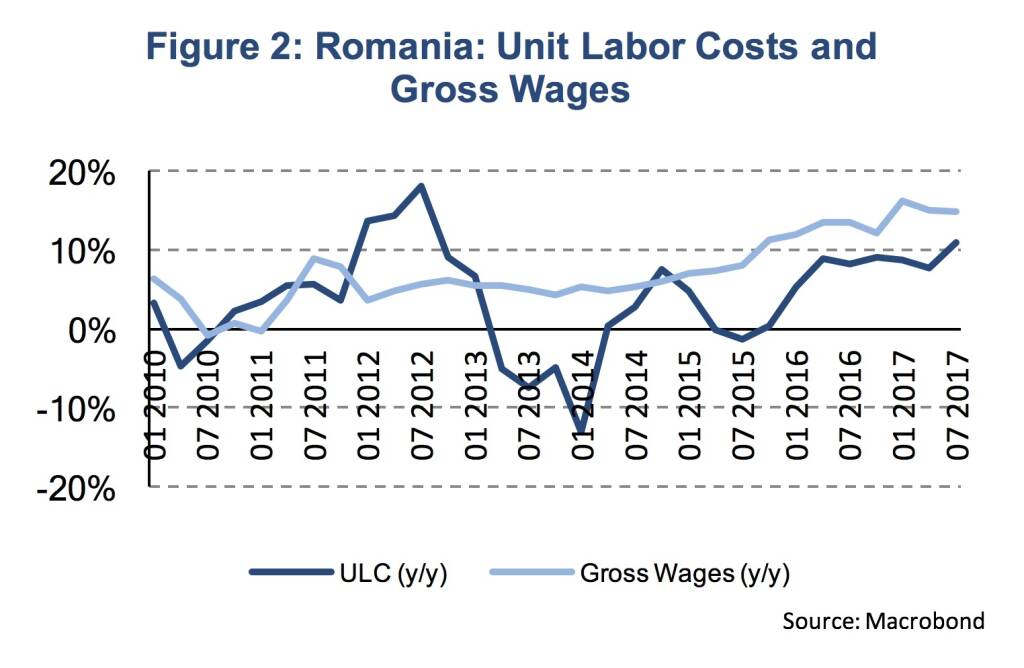
Inflation is driven by a broad set of product groups, with core inflation being the main contributing factor. The NBR’s CORE2 inflation measure was at 2.6 % (y/y) in November, after 2.1 % in October and 1.8 % in September. However, domestic price pressure to emerge can hardly be seen as a surprise. The Romanian economy expanded by 8.6 % (y/y, sa) in Q3 2017 after 6.1 % in Q2 and 5.8 % in Q1. At the same time, strong growth in gross wages (14.8 %, y/y, Q3) and unit labor costs (10.9 %, y/y, Q3) have already indicated increasing upward pressure on prices (Figure 2).
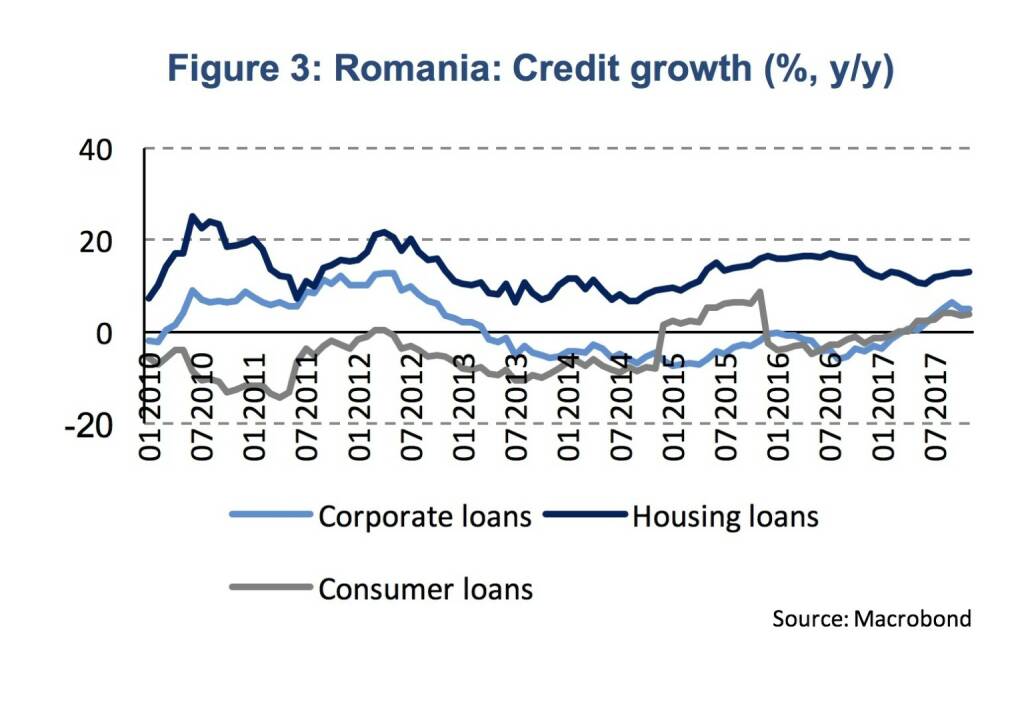
Hence, the National Bank of Romania can hardly be seen as proactive. Monetary conditions even became less accommodative well before the NBR tightened monetary policy. The 3 months interbank rate (ROBOR) went up by 90 bp already between mid-September and the beginning of 2018, so well before the NBR decided to increase its monetary policy rate. Credit growth shows a first halt in its upward trend. Loans to non-financial corporations expanded by 5 % (y/y) in October and November after 6.4 % in September. A similar pattern can be seen for consumer loans while housing loans regained some momentum lately (Figure 3).
Authors
Martin Ertl Franz Zobl
Chief Economist Economist
UNIQA Capital Markets GmbH UNIQA Capital Markets GmbH
Latest Blogs
» SportWoche Podcast #105: Lisa Reichkendler...
» Börse-Inputs auf Spotify zu u.a. Beiersdor...
» BSN Spitout Wiener Börse: Erste Group über...
» Österreich-Depots: Weekend-Bilanz (Depot K...
» Börsegeschichte 19.4.: Rosenbauer (Börse G...
» Aktienkäufe bei Porr und UBM, News von VIG...
» Nachlese: Warum CA Immo, Immofinanz und RB...
» Wiener Börse Party #633: Heute April Verfa...
» Wiener Börse zu Mittag schwächer: Frequent...
» Börsenradio Live-Blick 19/4: DAX eröffnet ...
Weitere Blogs von Martin Ertl
» Stabilization at a moderate pace (Martin E...
Business and sentiment indicators have stabilized at low levels, a turning point has not yet b...
» USA: The ‘Mid-cycle’ adjustment in key int...
US: The ‘Mid-cycle’ interest rate adjustment is done. The Fed concludes its adj...
» Quarterly Macroeconomic Outlook: Lower gro...
Global economic prospects further weakened as trade disputes remain unsolved. Deceleration has...
» Macroeconomic effects of unconventional mo...
New monetary stimulus package lowers the deposit facility rate to -0.5 % and restarts QE at a ...
» New ECB QE and its effects on interest rat...
The ECB is expected to introduce new unconventional monetary policy measures. First, we cal...
